Share this
Data Retention Best Practices
by Sean Curiel on Jan 7, 2021 8:00:00 AM
 Data grows at an astronomical rate and if not properly managed, can cost your company a hefty price tag in terms of storage, management, and liability. Understanding what type of data you are collecting, how frequently it is being accessed, and how long you must keep your retention data, are the basic elements of knowledge required to develop a data retention strategy for your business. Data that contains private customer information (such as PHI) may require special treatment when it comes to retention. And while data protection laws often dictate what data must be kept and for how long, they also often require businesses to remove specific data called retention data, after a certain period of time. These basic housekeeping steps to determine legal requirements as well as practical business needs, will help form the foundation of your data retention strategy.
Data grows at an astronomical rate and if not properly managed, can cost your company a hefty price tag in terms of storage, management, and liability. Understanding what type of data you are collecting, how frequently it is being accessed, and how long you must keep your retention data, are the basic elements of knowledge required to develop a data retention strategy for your business. Data that contains private customer information (such as PHI) may require special treatment when it comes to retention. And while data protection laws often dictate what data must be kept and for how long, they also often require businesses to remove specific data called retention data, after a certain period of time. These basic housekeeping steps to determine legal requirements as well as practical business needs, will help form the foundation of your data retention strategy.
Preparatory steps:
- Classify your data into types
- Determine what data is private / contains personally-identifying information
- Understand your legal requirements (HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA, FERPA, etc.)
What is Data Retention?
Data retention refers to your company's policy regarding how long retention data will be stored and/or archived as well as removed when no longer required, to meet legal, operational, and regulatory compliance.
Today, it is important for organizations to remember to not store data longer than what is required. According to the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) journal written by Lorrie Luellig, J.D., and Jake Frazier from IBM, “A lack of insight into what information needs to be kept, has led many organizations to accumulate mountains of electronically generated debris in the form of excess applications, servers, storage and backup tapes that no longer have any utility.”
69% of Data Collected Has Little or No Value
According to a recent IDC report, the amount of data stored globally is doubling every four years. It is expected to reach 8.9 ZB by 2024. Yet a surprisingly small percentage of this data is considered business critical. The exponential growth of data collection has created a problem as a vast majority of data (dubbed "dark data") sits unused. It's generally unseen by users as it may be unstructured and disorganized. It may create unnecessary costs in terms of resources that could be better focused in more important areas. In a survey of corporate CIOs and general counsels conducted at the Compliance, Governance and Oversight Council (CGOC)1 summit, it was found that 69 percent of all the data collected and maintained by most organizations had no business, legal, or regulatory value at all.
While regulatory compliance is often cited as the reason for dark data, the truth is that an overabundance of dark data may be caused by data mismanagement, poor communication, or a data-hoarding mindset. Dark data also represents risks beyond just unnecessary costs. With new data regulations appearing (GDPR, CCPA, etc), the need to remove specific data over time is also necessary to maintain compliance.
Implementing Data Retention Best Practices
So it's time to get a handle on this "dark data". Understanding what your organization is working with through mapping and classification of your retention data is the first step. Classifying the data that you are collecting is a matter of law (GDPR). It's wise to compare the legal regulations that you are required to uphold to understand their similarities and differences. Your classified data sets can then be assigned a risk level, and through the identification of your minimal requirements, a policy for this data can be created.
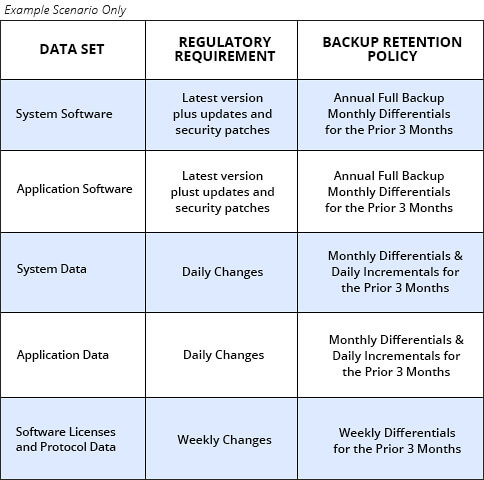
To purge redundant, and identify irrelevant data, we must have a data retention strategy. It's time to define what retention data will be retained for how long, and at what point it will be removed. This policy directly affects your backup jobs and must be supported in the features of your backup solution.
- Assemble your Data Retention Team
- Determine and Communicate Your Policy
- Revisit the Policy Regularly for Changes
NovaBACKUP makes it easy to implement your data retention policy through our backup software solutions. You can set up a custom data retention schedule so that only necessary backup data is stored. As every business is different, software flexibility to fine-tune adjustments is important. You can select how many valid backups to keep and for how long. Select what types of backups you wish to retain (file backups, image backups, incremental and differential backups). A few good rules of thumb to follow regarding your data retention include:
- Keep your policy as simple and easily explainable as possible
- Cater your policy to legal regulatory requirements
- Keep personal customer data for no longer than necessary
- Move critical data to fast, accessible storage
To defend against cyber threats like ransomware, multiple copies of data are often required. Using NovaBACKUP's data retention functionality gives backup administrators direct control over what backup data is retained and for how long. You can meet your business, financial, legal, and regulatory needs for data retention with fast, efficient software and a few good policies. Speak to one of our backup experts today to assist with your data retention strategy.
1Lorrie Luellig, J.D., and Jake Frazier, J.D. "A COBIT Approach to Regulatory Compliance and Defensible Disposal." https://www.isaca.org. ISACA JOURNAL, VOLUME 5, 2013. Web. 26 SEP. 2014.
Share this
- Pre-Sales Questions (112)
- Tips and Tricks (95)
- Industry News (60)
- Reseller / MSP (37)
- Security Threats / Ransomware (29)
- Applications (28)
- Best Practices (26)
- Cloud Backup (25)
- Backup Videos (24)
- Disaster Recovery (24)
- Compliance / HIPAA (23)
- Storage Technology (21)
- Virtual Environments (17)
- Technology Updates / Releases (9)
- Infographics (8)
- Backup preparation (3)
- Company (US) (1)
- Events (1)
- Events (US) (1)
- Products (US) (1)
- March 2024 (2)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (1)
- December 2023 (1)
- November 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (1)
- September 2023 (1)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (3)
- December 2022 (1)
- November 2022 (2)
- October 2022 (2)
- September 2022 (2)
- August 2022 (2)
- July 2022 (1)
- June 2022 (1)
- April 2022 (1)
- March 2022 (2)
- February 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (1)
- December 2021 (1)
- November 2021 (1)
- September 2021 (1)
- August 2021 (1)
- July 2021 (1)
- June 2021 (2)
- May 2021 (2)
- April 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (2)
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (2)
- December 2020 (1)
- November 2020 (1)
- October 2020 (2)
- September 2020 (4)
- August 2020 (2)
- July 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (1)
- March 2020 (3)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (2)
- December 2019 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- October 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (1)
- June 2019 (1)
- April 2019 (1)
- February 2019 (1)
- January 2019 (1)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (2)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (4)
- June 2018 (2)
- April 2018 (2)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (3)
- December 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (2)
- April 2017 (5)
- March 2017 (4)
- February 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (1)
- November 2016 (1)
- October 2016 (2)
- September 2016 (1)
- August 2016 (3)
- July 2016 (2)
- June 2016 (3)
- May 2016 (7)
- April 2016 (8)
- March 2016 (1)
- February 2016 (3)
- January 2016 (12)
- December 2015 (7)
- November 2015 (6)
- October 2015 (6)
- September 2015 (2)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (2)
- June 2015 (2)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (5)
- March 2015 (3)
- February 2015 (4)
- January 2015 (2)
- October 2014 (5)
- September 2014 (8)
- August 2014 (5)
- July 2014 (8)
- June 2014 (5)
- May 2014 (5)
- April 2014 (9)
- March 2014 (7)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (5)
- December 2013 (5)
- October 2013 (7)
- September 2013 (2)
